Command Line Interface
Encord Active is equipped with a command line interface (CLI) that simplifies your interaction with the platform. With the CLI, you can easily initialize projects, import projects and labels, manage and run metrics, and launch the application.
We strive to ensure that our CLI is self-explanatory, eliminating the need for frequent switching between the terminal and documentation.
Simply run encord-active --help to get details about all the top-level commands and encord-active COMMAND --help
Here is a list of all the top-level commands:
quickstart Start Encord Active straight away 🏃💨
download Download a sandbox dataset to get started 📁
init Initialize a project from your local file system 🌱
import Import projects or predictions ⬇️
refresh Sync data and labels from a remote Encord project 🔄
start Launch the application with the provided project ✨
project Manage project settings ⚙️
metric Manage project metrics 📋
print Print useful information 🖨️
config Configure global settings 🔧
quickstart
The command will download a small example project to a subdirectory named quickstart in the current working directory and automatically launch the application.
Usage: encord-active quickstart [OPTIONS]
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Directory where the project would be saved.
download
In addition to the quickstart example, there are a several other open-source datasets available for download that you can use to explore the capabilities of Encord Active.
The command will display a list of available sandbox projects, allowing you to select one from the menu interactively.
If you prefer to skip the interactive selection, you can directly specify the sandbox project name using the --project-name optional argument.
Usage: encord-active download [OPTIONS]
Options:
--project-name TEXT Name of the chosen project.
--target -t DIRECTORY Directory where the project would be saved.
List of downloadable sandbox projects
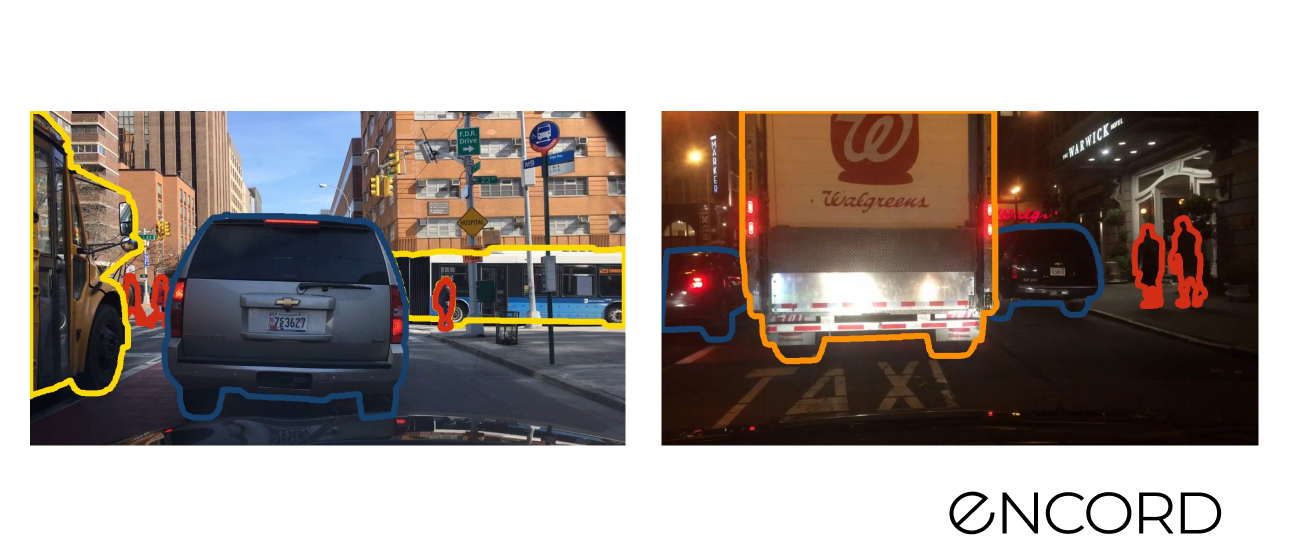
Berkeley Deep Drive
- Research Paper: BDD100K: A Diverse Driving Dataset for Heterogeneous Multitask Learning
- Authors: Fisher Yu, Haofeng Chen, Xin Wang, Wenqi Xian, Yingying Chen, Fangchen Liu, Vashisht Madhavan, Trevor Darrell
- Dataset Size: 1000 images & 12973 annotations
- Categories: 8 classes
- License: BSD 3-Clause License
- Release: 21st September, 2020
- Read more: Webpage & GitHub
Sample pictures:

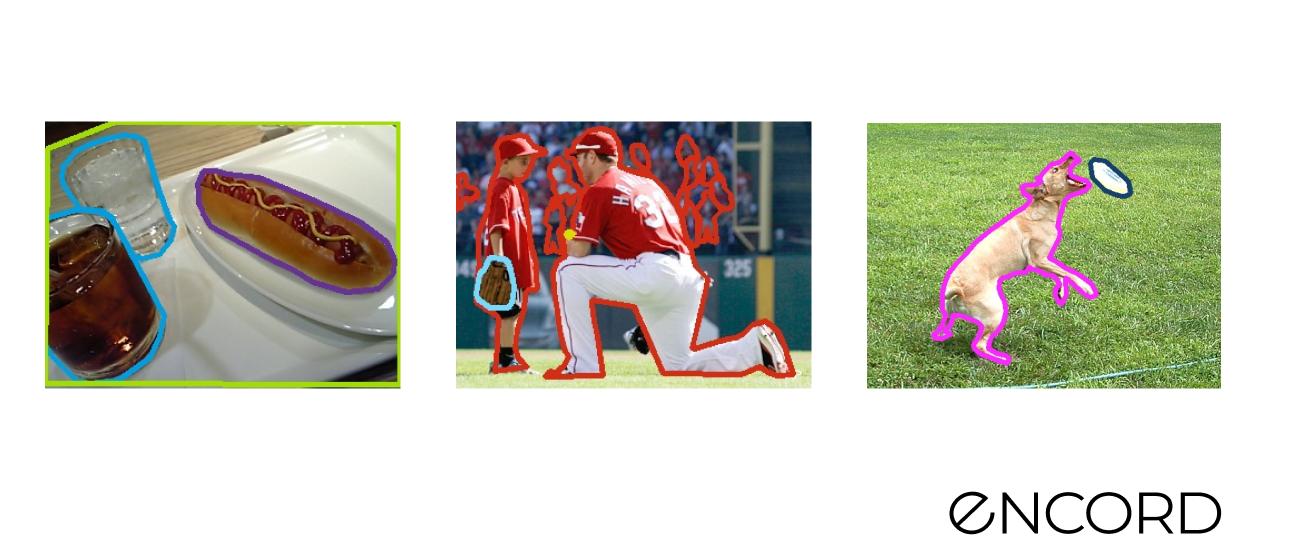
COCO Validation 2017 Dataset
- Research Paper: Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context
- Author: Tsung-Yi Lin , Michael Maire, Serge Belongie, Lubomir Bourdev , Ross Girshick, James Hays, Pietro Perona, Deva Ramanan, C. Lawrence Zitnic, Piotr Dollár
- Dataset Size: 5000 images, 4784 annotations
- Categories: 81 classes
- License: CC BY 4.0
- Release: 1st, May, 2014
- Read More: GitHub & Webpage
Sample pictures:

Covid 19 Segmentation Dataset
- Research Paper: Unknown
- Author: Unknown
- Dataset Size: 100 images & 602 annotations
- Categories: 13 classes
- License: CC BY 4.0
- Release: Unknown
- Read more: GitHub
Sample pictures:
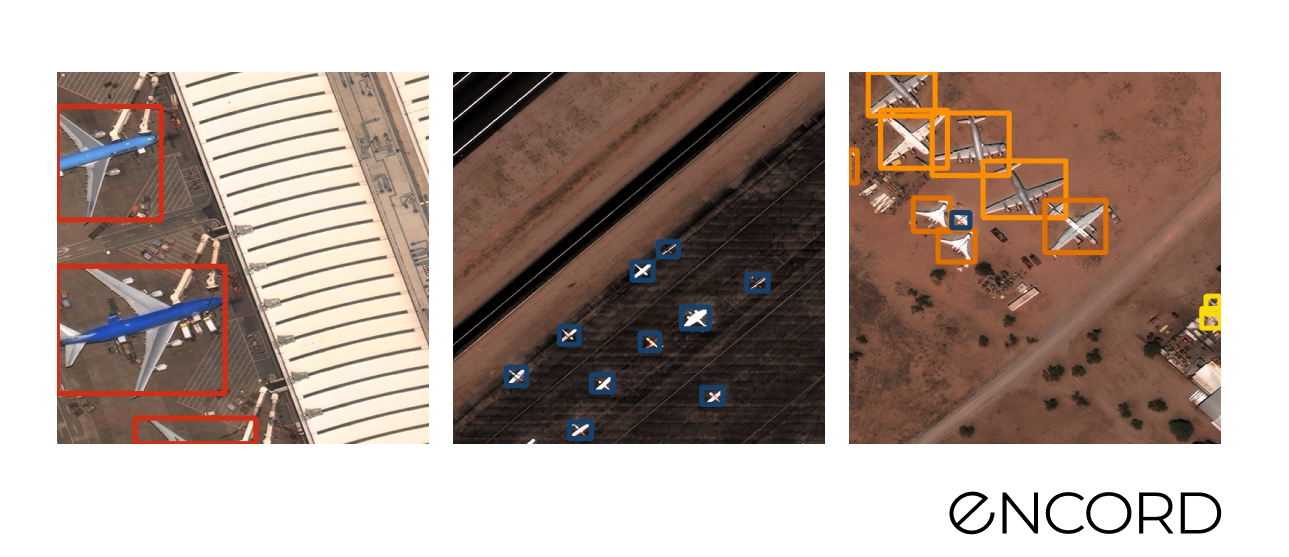
Rareplanes
- Research Paper: RarePlanes: Synthetic Data Takes Flight
- Author: Jacob Shermeyer, Thomas Hossler, Adam Van Etten, Daniel Hogan, Ryan Lewis, Daeil Kim
- Dataset Size: 2710 images & 6812 annotations
- Categories: 7 plane categories
- License: CC 4.0 BY SA
- Release: 4 June, 2020
- Read More: Webpage
Sample pictures:

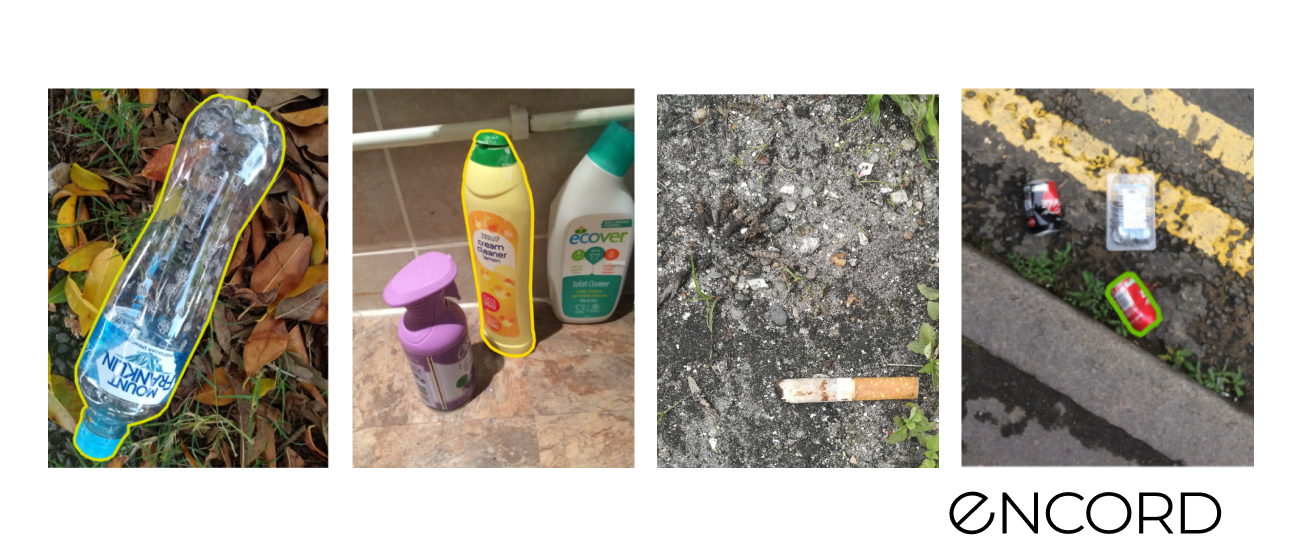
TACO Dataset
- Research Paper: TACO: Trash Annotations in Context for Litter Detection
- Author: Pedro F Proença, Pedro Simões
- Dataset Size: Official: 1500 images, 4784 annotations & Unofficial: 3736 images, 8419 annotations
- Categories: 60 litter categories
- License: CC BY 4.0
- Release: 17th, March, 2020
- Read More: GitHub & Webpage
Sample pictures:

Limuc Ulcerative Colitis Classification
- Research Paper: Improving the Computer-Aided Estimation of Ulcerative Colitis Severity According to Mayo Endoscopic Score by Using Regression-Based Deep Learning
- Authors: Gorkem Polat, MSc, Haluk Tarik Kani, MD, Ilkay Ergenc, MD, Yesim Ozen Alahdab, MD, Alptekin Temizel, PhD, Ozlen Atug, MD
- Dataset Size: 11276 images
- Categories: Medical (Endoscopy/Colonoscopy)
- License: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
- Release: 14th March 2022
- Read more: Webpage & GitHub
start
Launch the application with the provided project ✨
Usage: encord-active quickstart [OPTIONS]
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path of the projects you would like to start
init
The command initializes new project from locally stored images and labels. It will search for images based on the data-glob arguments. By default, all jpeg, jpg, png, and tiff files will be matched.
It will search for labels as well if the label-glob and transformer options are provided.
Both glob results will be passed to your implementation of the LabelTransformer interface if you specify the transformer argument.
Usage: encord-active init [OPTIONS] ROOT
Arguments:
* root DIRECTORY The root directory of the dataset you are trying to import
Options:
--data-glob -dg TEXT Glob pattern to choose files. Repeat the `--data-glob` argument to
match multiple globs.
--label-glob -lg TEXT Glob pattern to choose label files. Repeat the `--label-glob`
argument to match multiple globs. This argument is only used if you
also provide the `transformer` argument.
--target -t DIRECTORY Directory where the project would be saved.
--name -n TEXT Name to give the new project. If no name is provided, the root
directory will be used with '[EA] ' prepended.
--symlinks Use symlinks instead of copying images to the target directory.
--dryrun Print the files that will be imported WITHOUT importing them.
--no-metrics Skip metrics execution on the initiated project.
--transformer PATH Path to python module with one or more implementations of the
`encord_active.lib.labels.label_transformer.LabelTransformer`
interface.
The Quick import data & labels workflow is a great starting point for utilizing this command.
import
The command is used to import projects and predictions from different sources.
Refer to the Import section for specific usage examples.
Usage: encord-active import [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Import Projects or Predictions ⬇️
Commands:
predictions Imports a predictions file. The predictions should be using the `Prediction` model
and be stored in a pkl file.
If the `--coco` option is specified then the file should be a json following the COCO results format. 🧠
project Imports a new project from Encord or a local COCO project. 📦
project
Imports a new project from Encord or a local COCO project.
Usage: encord-active import project [OPTIONS]
Encord Project Arguments:
--project-hash TEXT Encord project hash of the project you wish to import.
Leaving it blank will allow you to choose one interactively.
--store-data-locally Store project data locally to avoid the need for on-demand download when visualizing and analyzing it.
COCO Project Arguments:
--coco Import a project from the COCO format.
--images -i DIRECTORY Path to the directory containing the dataset images.
--annotations -a FILE Path to the file containing the dataset annotations.
--symlinks Use symlinks instead of copying COCO images to the target directory.
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Directory where the project would be saved.
predictions
Imports a predictions file. The predictions should be using the Prediction model and be stored in a pkl file.
If the --coco option is specified then the file should be a json following the COCO results format.
Refer to the Import model predictions section for specific usage examples.
Usage: encord-active import predictions [OPTIONS] PREDICTIONS_PATH
Arguments:
* predictions_path FILE Path to a predictions file.
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
--coco Import a COCO results format file.
refresh
Sync data and labels from a remote Encord project.
Usage: encord-active refresh [OPTIONS]
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
The local project should have a reference to the remote Encord project in its config file (project_meta.yaml).
The required attributes are:
- The remote flag set to
true. - The hash of the remote Encord project.
- The path to the private Encord user SSH key.
This command works in local projects created via encord-active import project and those successfully exported to Encord from the "Actions" tab in the UI's toolbox.
project
Manage project settings ⚙️
Usage: encord-active project [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Commands:
download-data Download all data locally for improved responsiveness.
download-data
Store project data locally to avoid the need for on-demand download when visualizing and analyzing it.
Usage: encord-active project download-data [OPTIONS]
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
metric
Manage project metrics.
Usage: encord-active metric [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Commands:
add Add metrics.
list List metrics.
remove Remove metrics.
run Run metrics.
show Show information about available metrics.
Make sure your shell's current working directory is that of an Encord Active project, or your command points to one with the --target global option.
add
Add metrics to the project by specifying the path to a metrics module and the titles of the desired metrics within the module. If no metric titles are provided, all metrics found in the Python module will be automatically added to the project.
Usage: encord-active metric add [OPTIONS] MODULE_PATH [METRIC_TITLE]...
Arguments:
* module_path FILE Path to the python module where the metric resides.
metric_title [METRIC_TITLE]... Title of the metric. Can be used multiple times.
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
If you attempt to add a metric that already exists, it will be skipped, and you will be notified accordingly. However, if a metric title is not found in the Python module, an error will occur. Please ensure that the metric titles are accurate and correspond to the metrics available in the module.
Some shells may treat square braces ([ and ]) as special characters. It is suggested to always quote arguments containing these characters to prevent unexpected shell expansion.
remove
Removes metrics from a project.
Usage: encord-active metric remove [OPTIONS] METRIC_TITLE...
Arguments:
* metric_title METRIC_TITLE... Title of the metric. Can be used multiple times.
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
list
List metrics in the project, including editables. Metrics are listed in a case-insensitive sorted order.
Usage: encord-active metric list [OPTIONS]
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
run
Run metrics on project data and labels.
Usage: encord-active metric run [OPTIONS] [METRIC_TITLE]...
Arguments:
metric_title [METRIC_TITLE]... Title of the metric. Can be used multiple times.
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
--all Run all metrics.
--fuzzy Enable fuzzy search in the selection. (press [TAB] or [SPACE] to select more than one) 🪄
show
Show information about one or more available metrics in the project.
Usage: encord-active metric show [OPTIONS] METRIC_TITLE...
Arguments:
* metric_title METRIC_TITLE... Title of the metric. Can be used multiple times.
Options:
--target -t DIRECTORY Path to the target project.
config
Encord Active keeps some configurable properties to prevent repetitive input prompts.
The config file is stored at:
- Linux:
~/.config/encord-active/config.toml - MacOS:
~/Library/Application Support/encord-active/config.toml - Windows:
%APPDATA%/encord-active/config.toml
ssh_key_path = "/absolute/path/to/ssh-key" # The API key to use when accessing remote Encord projects
Usage: encord-active config [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Commands:
get Print the value of an Encord Active configuration property.
list List Encord Active configuration properties.
set Sets an Encord Active configuration property.
unset Unsets the value of an Encord Active configuration property.
print
Print useful information.
Usage: encord-active print [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Commands:
data-mapping Prints a mapping between `data_hashes` and their corresponding `filename`.
encord-projects Print the mapping between `project_hash`es of your Encord projects and their titles.
ontology Prints an ontology mapping between the class name to the `featureNodeHash` JSON format.
system-info Prints the information of the system for the purpose of bug reporting.
Options:
--json Save output to a json file.